AI in Marketing & Sales: Revolutionizing Business Growth
|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Understanding AI in Marketing
AI in marketing helps you analyze customer data, automate tasks, and create personalized experiences. With machine learning in marketing, AI can predict trends, optimize campaigns, and improve targeting. Businesses use AI for digital marketing to run smarter ad campaigns, segment customers more effectively, and refine messaging based on real-time insights.
How AI Powers Personalization at Scale
Personalization goes beyond addressing customers by name. AI digital marketing tools analyze browsing behavior, purchase history, and engagement patterns to deliver tailored recommendations.
Customer segmentation using AI helps you group audiences based on their interests and buying habits, making your campaigns more relevant. AI-driven customer experiences solutions, like chatbots and recommendation engines, improve interactions by responding in real time.
-
Enhancing Customer Experience
Anomaly detection at scale can help detect changes in a consumer’s behavior compared to self, to similar customer profiles, and to the overall customer set. The negative experience can be detected through a customer’s changes in ordering patterns even without capturing direct feedback. Algorithms can identify a change in buying patterns; for instance, a reduction of sales in a product category (e.g., produce) can trigger alerts to an underlying problem. Further machine learning can diagnose deeper connections: Is the anomaly connected with store sales pattern, day of the week, supplier, weather, operational conditions like labor staffing, or a combination? AI can also power next-best-action recommendations for customers, enhancing the overall customer experience.
A study by Harvard Business Review found that customers who enjoy positive experiences are likely to remain customers for five years longer than customers who have negative experiences. In addition, delivering positive customer experiences can reduce your cost of serving customers by up to 33%.
-
AI-Driven Sales Automation
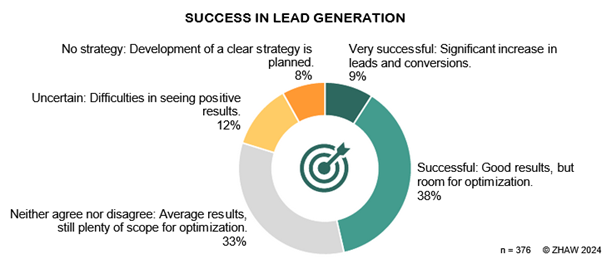
Lead generation is about identifying potential customers and collecting contact data plus interests in specific products or services. One question in the online survey asked 385 companies from Switzerland and Germany about their current lead generation strategy, with one-tenth describing themselves as very successful (see Figure 6). In these cases, the number of leads and conversions had increased significantly. The majority of respondents describe themselves as successful (38%) – achieving good results but still seeing potential for optimization.
Every third company rates itself as “neither successful nor unsuccessful,” average but with potential – an observation that has seen an 11 percent year-on-year decline. This interesting development indicates that awareness of and reflection on lead generation are increasingly common in corporate practice.
Figure 6
One-fifth of the companies surveyed stated they were unsure about lead generation. Twelve percent in Figure 6 admit difficulties in seeing positive results in lead generation. Eight percent of companies do not have a lead management strategy.
Compared to the previous year, there was a slight increase of two percent among companies that consider themselves “very successful” and four percent among companies without a clear strategy. The proportion of those who consider themselves “uncertain” also rose by three percent. These findings show that despite some improvements, there are still challenges in the area of lead generation. There is an obvious need for more effective strategies and measures to meet the challenges successfully and increase the performance of companies in this area. From the perspective of the companies surveyed, two different tools work best, on average, to generate new leads.
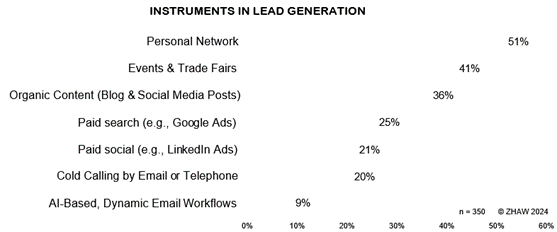
As shown in Figure 7 below, over half of the companies surveyed use their personal network for lead generation, followed by events and trade fairs at 41 percent. Unlike in the previous year, events and trade fairs surpassed the relevance of organic content with an increase of ten percent. The use of personal networks also increased by six percent compared to 2023. This is known as the post-COVID effect, with personal contacts – the “personal network” and “events & trade fairs” – once again becoming the most essential tool for lead generation after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Around a third of respondents use organic content via social media posts and blogs for lead generation. For many practitioners, paid search (above all Google Ads with 25% of mentions) and paid social (especially LinkedIn Ads with 21% of mentions) work best for generating leads. One in five companies surveyed also employed cold calling, for example, by email or telephone.
Nine percent of the companies surveyed stated that AI-based, dynamic email workflows work best for generating new leads – two percent more than in the previous year. AI-driven sales automation has received increasing attention and triggered discussions in recent years, particularly concerning its potential applications and effects on marketing and sales. At the same time, automated, dynamic email workflows have established themselves as tools in marketing strategies, and their scope of application has been steadily expanded over several years. Despite these developments, there still seems to be great reluctance or at least a degree of skepticism regarding the effectiveness of AI-based approaches in lead-generation contexts. One possible explanation for this phenomenon may lie in the complexity and multi-layered nature of the lead generation process, which traditionally depends on various factors. These include the industry, business model, pricing and sales strategy, products and services offered, and individual consumer preferences.
Figure 7
-
Predictive Analytics in Sales
Traditionally, AI in sales was limited in scope, executing tasks based on explicitly stated rules. As AI has evolved from executing tasks to tackling more complex problems, “telling machines what to do” has shifted to “helping machines learn what to do.” These enhanced machine learning (ML) capabilities can be applied to sales data and analytics in the following ways:
- Diagnostic analytics analyzes correlations between variables in a dataset to find existing relationships between them. The established relationships between variables in the captured data can be used to analyze problems and cluster data for sales purposes, such as personalization, segmentation, and tiering.
- Predictive analytics tries to estimate what will happen in the future. It does so by identifying the factors that influence a given outcome and understanding how they do so. This behavior is distinct from diagnostic analytics, which only tries to explain why something happens. Sales forecasting commonly uses predictive models to inform pipeline planning — for example, predicting next month’s sales bookings by uncovering trends and seasonal patterns in the sales data.
- Optimization and prescriptive analytics go beyond predicting outcomes and recommend the next action(s) to take for a given prediction. This form of analytics prescribes the best course of action when making a complex decision that involves trade-offs between business objectives and constraints. It’s also commonly referred to as a recommender/next-best-action system because it identifies and suggests cross-sell and upsell opportunities in accounts to sellers and sales managers.
To take advantage of more predictive and prescriptive sales AI in the short term, sales leaders need to invest in data science specialists to envision, develop, and harness the potential of AI innovations. However, many of the specialized skills these experts provide will soon be replaced by automated analytics ecosystems — and the need for data scientists will evolve toward a higher-ROI delivery model that applies only to the most complex and unstructured sales problems.
No longer a one-size-fits-all solution, AI in sales can enhance decision-making by flagging patterns and forecasting broad outcomes better than humans can do. For example:
- District and region leaders will become better strategists and coaches as AI sales automation tools enable them to synthesize customer needs at the district, territory, account, and opportunity levels simultaneously.
- Sellers themselves will make better short- and long-term decisions, as augmented analytics deliver data-led decision support at the portfolio, account, and opportunity level. Intelligent decision support will help sellers make the most of their human judgment (and will quickly weed out sellers who lack those capabilities).
-
Generative AI-Powered Marketing Automation
Generative AI in marketing is making it possible to revolutionize consumer marketing as we currently know it. At an individual-company level, marketing campaigns that once required months of content design, insight generation, and customer targeting can now be rolled out in weeks or even days, often with at-scale personalization and automated testing. Website development and customer service tasks are often the bottlenecks in interactions with individual consumers, but when executed well, they can induce greater engagement and improve satisfaction. Marketers can simultaneously analyze and interpret text, image, and video data to better understand innovation opportunities. Marketing automation with AI is powering granular personalization in ways that just weren’t possible before.
In the world of marketing, fine-tuning an existing generative AI model might mean training an open-source model with proprietary data (for example, brand guidelines or historical-marketing-campaign creatives) to generate bespoke content. This semi-custom generative AI solution can be regularly updated with new company data and ongoing learning. The result is a continually improving, bespoke generative AI solution that helps increase a company’s competitive advantage as it develops.
-
Targeted Advertising and Customer Segmentation
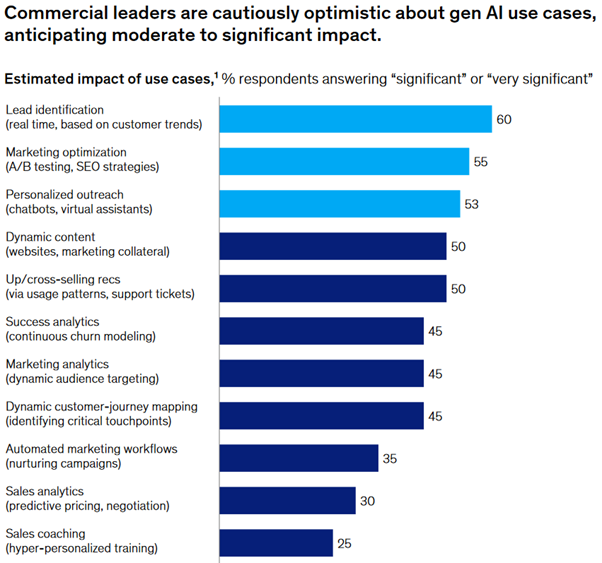
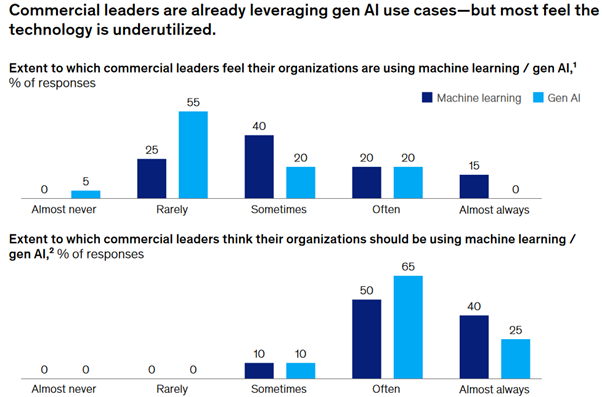
The team at McKinsey asked a group of commercial leaders to provide their perspective on use cases and the role of generative AI in marketing and sales more broadly. Notably, they found cautious optimism across the board: respondents anticipated at least moderate impact from each use case suggested. These players are most enthusiastic about use cases in the early stages of the customer journey lead identification, marketing optimization, and personalized outreach.
Various players are already deploying generative AI use cases, but this is undoubtedly only scratching the surface. Researchers at McKinsey found that 90 percent of commercial leaders expect to utilize generative AI solutions “often” over the next two years.
Real-World Examples of AI in Marketing
Businesses are already using AI marketing automation tools to improve efficiency. Here’s how:
- AI for advertising adjusts ad placements based on user engagement, reducing wasted ad spend.
- Generative AI in marketing creates personalized emails, product descriptions, and social media content at scale.
- AI sales automation prioritizes high-potential leads, allowing sales teams to focus on conversions.
- Predictive analytics in sales forecasts demand, helping businesses plan inventory and promotions.
Challenges and Considerations
While marketing AI offers many benefits, there are challenges:
- Data privacy: AI relies on large datasets, raising concerns about customer data use.
- Bias in AI: AI may make inaccurate predictions if training data is not diverse.
- High implementation costs: Businesses need the right tools and expertise to integrate AI effectively.
- Dependence on quality data: Inaccurate or outdated data can affect AI’s performance.
The Future of AI in Marketing and Sales
As AI evolves, expect more automation, real-time personalization, and predictive insights. Businesses using AI in digital marketing will gain a competitive edge by delivering better experiences and improving efficiency. AI will continue shaping AI marketing automation, AI for advertising, and predictive analytics in sales, making marketing more precise and results-driven.
FAQs
How is AI used in marketing?
AI in marketing helps businesses analyze data, automate tasks, and enhance customer interactions. AI digital marketing solutions like AI marketing automation tools optimize ad targeting, personalize content, and improve customer segmentation using AI for better engagement.
How does AI improve the efficiency of marketing campaigns?
AI in digital marketing automates repetitive tasks, predicts customer behavior, and optimizes ad spend. Generative AI in marketing creates personalized content, while AI for advertising ensures better audience targeting. Marketing AI enhances decision-making using machine learning in marketing for real-time insights.
What are the main benefits of using AI in marketing and sales?
Some benefits of using AI in marketing and sales are:
- AI sales automation reduces manual efforts in lead generation and follow-ups.
- Predictive analytics in sales helps businesses anticipate customer needs.
- AI-driven customer experience improves engagement through chatbots and personalized recommendations.
AI marketing automation streamlines workflows, increasing efficiency.
How can AI help businesses understand customer behavior better?
Customer segmentation using AI groups audiences based on real-time data, enabling hyper-targeted marketing. Machine learning in marketing identifies patterns in customer preferences, while predictive analytics in sales forecasts buying behavior for better engagement strategies.
What are the key challenges businesses face when integrating AI into marketing and sales?
Some key challenges businesses face when integrating AI into marketing and sales are:
- High implementation costs for AI marketing automation tools.
- Data privacy concerns when using AI in marketing.
- Need for skilled professionals to manage AI for digital marketing solutions.
- Ensuring AI-generated content aligns with brand voice.
How does AI personalize customer experiences in marketing?
AI-driven customer experience solutions analyze past interactions to deliver tailored content, product recommendations, and chatbot responses. AI for advertising dynamically adjusts campaigns based on user engagement, while AI in digital marketing tools automates personalized email and social media strategies.
What are the ethical implications of using AI in marketing and sales?
The ethical implications of implementing AI in marketing and sales are:
- AI marketing automation raises concerns about data security and consumer privacy.
- Bias in machine learning in marketing can lead to unfair targeting.
- Transparency issues in AI-driven customer experience can impact trust.
- Over-reliance on AI for digital marketing may reduce human creativity in campaigns.
Author: Shreya Garg