What Is Big Data? Characteristics That Define It
Big data is a term used to denote structured and unstructured chunks of information embedded in various sources that a business is flooded every day. Some part of the data might be useful for business decision-making and some could be completely useless. Any organization could have huge amounts of useless data that adds no value to the core business. Big data can be used for analysis of insights which helps a decision-maker in taking long-term strategic moves. In simplest terms, big data helps to pick and choosing relevant information from the data which is eventually used by the organizations in decision-making.
Data sets consist of hidden information which could be crucial for a business’s long-term growth. There are embedded patterns, trends and association within the data sets. The extremely large chunk of data that could be used in order to reveal such relationships and patterns related to human behaviours and interactions is known as big data.
There are a few data sets which are so large that the traditional data processing application software could not process them. With a passage of time, information technology has evolved a lot. Due to this, a large amount of data could be stored in smaller devices. Even though the terminology of big data is newer, still the concept is age-old.
The three V’s of big data could be as under:
Volume
The volume of data collected by the organizations is huge since it is collected from a variety of sources like historic business transactions, social media, databases, and machine-to-machine data. The storage could have been an issue in the past, but with progress in IT and introduction of new technologies like Hadoop have eased the burden.
Velocity
The big data is available in real-time. The data streams at an unprecedented pace, and hence it should be dealt in a timely manner.
Variety
Big data comes in different formats like structured, numeric, and traditional databases through pictures, audio files, emails, videos, and financial transactions.
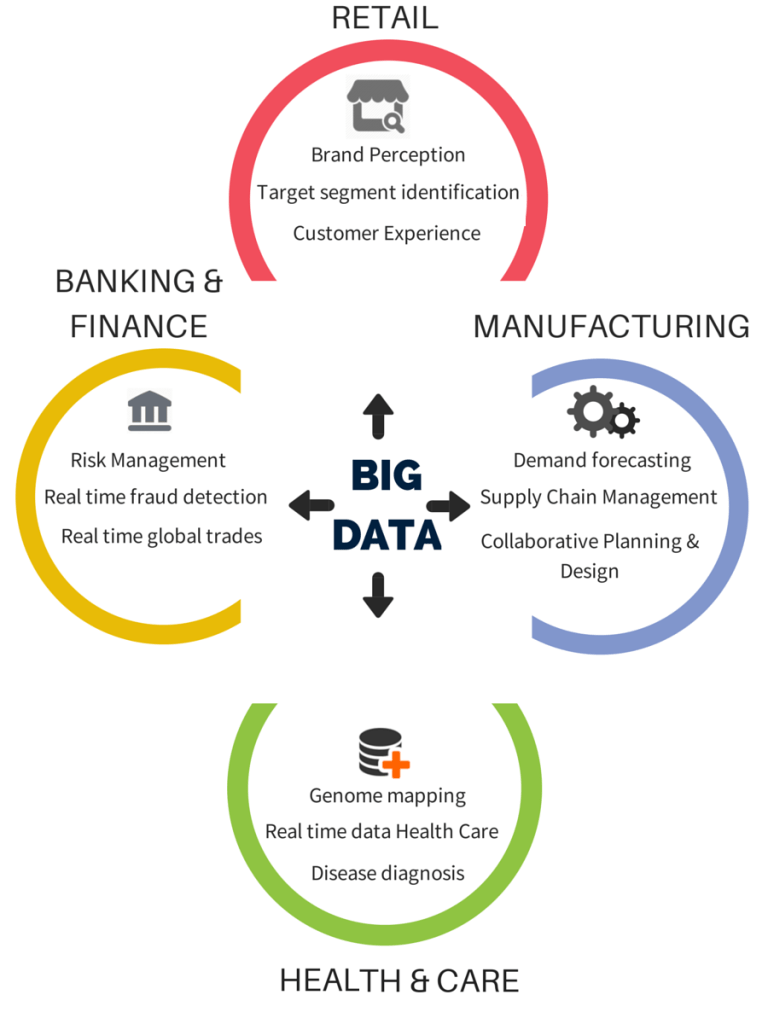
Big data provides specific benefits to businesses working in various industries. The most common industries that have benefitted from big data are as follows:
The database management through big data helps in big data analysis.
Retail Sector
Big data helps in perceiving the brand and target segment identification through analysis of data related to customer experience.
Manufacturing Sector
Various processes in manufacturing like demand forecasting, supply chain management, logistics management, and collaborative planning could be assessed by taking the assistance of big data.
Healthcare Sector
Processes like diagnosis and patient management is ensured through genome mapping.
Banking & Finance
The banking and finance sector is prone to a number of risks and frauds which are ought to be tracked and monitored at a constant basis. Big data analytics help in ensuring that the database management is streamlined, and a dedicated team is working to take care of the most crucial business threats.
In the past couple of years, the overall importance of this concept has increased consistently. Even though there are a number of critics that have claimed that big data is over-hyped and fails to deliver value to the organization when it matters the most; but at the same time, there are a number of case studies where this process has helped the organizations (and persons) in achieving unprecedented results. As of now, the large and medium-sized businesses are benefitted the most from the usage of big data analytics. However, it is presumed that the small businesses shall be able to reap the benefits arising from big data process in the future.
Characteristics of Big Data
Big data could be a term used to denote data which is not only huge in size but also grows at rapid pace in a short span of time. It is too huge and grows exponentially at rapid speeds in such a manner that the traditional data processing tools are unable to derive meaningful information from it by processing. Some of the most common and popular examples of big data have been quoted as under:
New York Stock Exchange
The largest stock exchange of the world generates more than one terabyte of new trade data every day. The total market capitalization of the companies traded on the exchange is close to $20 trillion. The average daily trading value exceeds $180 billion per day.
Facebook looks a friendly and harmless social network and has become part of our lives ever since it was introduced some thirteen years ago. However, the volume of data generated by Facebook is more than 500 terabytes per day. Every time you click a selfie and post it on social network, the total data generated increases. The data is also generated through videos, messages, blog posts, and even likes and comments.
The big data could be broadly categorized into three main parts:
1. Structured Data
The data which could be stored and accessed in a fixed format could be described as ‘structured’. With development in Information Technology, new methods have been innovated to help the users for working with this data. The data has grown to considerable point, with the typical range going beyond multiple zettabytes .
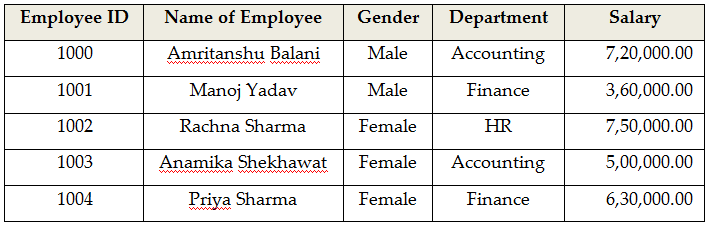
Structured data as described in a database could be illustrated as follows:
2. Unstructured Data
The data which does not have specific format or structure could be described as unstructured data. Besides being huge in size and unmanageable, the unstructured data poses various challenges in deriving meaningful information and value out of it. A combination of files, videos, numbers, and images could be considered as unstructured data. For illustration, this (Google Search Result) could be an example of big data:
3. Semi Structured Data
It could include both types of data. The data could be seen as structured but it does not make any sense unless it is processed through a software program. The data represented in an XML file could be an example of semi-structured data.
The most important characteristics of Big Data have been explained as follows:
• Volume
Big data is a synonym for huge volumes of data. Since the data is now created by machines at a greater pace than ever before, the overall volume is beyond traditional measurement methods.
• Variety
Variety refers to different types of data: structured, unstructured, and semi-structured from various sources which is stored at different storage locations.
• Velocity
With improvement and growth in information technology, the overall pace at which data is stored and processed has increased at an unprecedented rate. Real-time data is available and it changes continuously. It purely depends on the ability of the organizations to tap out the benefits from such fast paced data.
• Veracity
It is crucial to keep away unwanted piece of information from the relevant data. However, veracity of data is one of the most important characteristics which any analyst would want to achieve.
• Validity
Various data analysts working in the field of big data management (like IBM) provide services that help with data veracity and validity to ensure only relevant part of information reaches to the intended users.
• Volatility
It refers to the period for which the data should remain valid. There is no point of storing the data beyond a point when it is expected to add no value to the business decision-making.